
Vedantu LIVE Online Master Classes is an incredibly personalized tutoring platform for you, while you are staying at your home. Also, you can try searching for complex numbers and quadratic equations solutions to tackle cumbersome topics.ĭownload our Vedantu app to learn amazing mathematics concepts with ease. However, you find solutions to these problems quickly if you understand the theorems well. Some chapters apart from quadratic equations can appear problematic to solve, such as integrals, permutation and combination, etc. If the real portion is R(z) and the imaginary section constitutes I(z) of the value z, then what will be the answer? Read the following question on complex numbers and quadratic equations thoroughly to excel in your studies.ġ. Hence, the equation is equal to 2x 2 – 4x + 3 = 0 Multiplication of them will result in (4 + 2)/4 = 3/2 Hence, the quadratic equation will be x 2 + 4x – 7 = 0
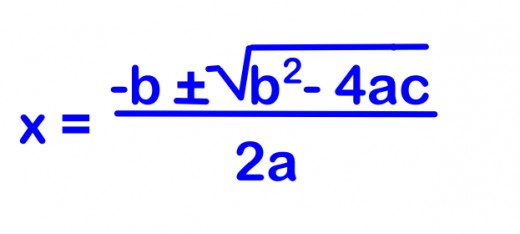

Multiplication of these roots is (-2 - i√3) * (- 2 + i√3) = - 3 - 4 = 7 Here, sum of the value of roots is -2 - i√3 - 2 + i√3 = - 4 Therefore, the equation is equal to x 2 – 2x + 5 = 0 Then, products of these roots will be (1 + 2i) * (1 – 2i) = 1 + 4 = 5 Sum of the value of roots is (1 + 2i) + (1 – 2i) = 2 Solution: Assume, (a + b) and (a – b) are roots for all the problems. Will be the Equation of the Following if they have Real Coefficients with One Root? and Quadratic Equationsīelow there is a complex numbers and quadratic equations miscellaneous exercise. Here the value of a is equal to zero since the equation is not quadratic.Įxercises on Complex Nos. However, can you ascertain the value of c? Well, the value of c = 0 as it is not present.

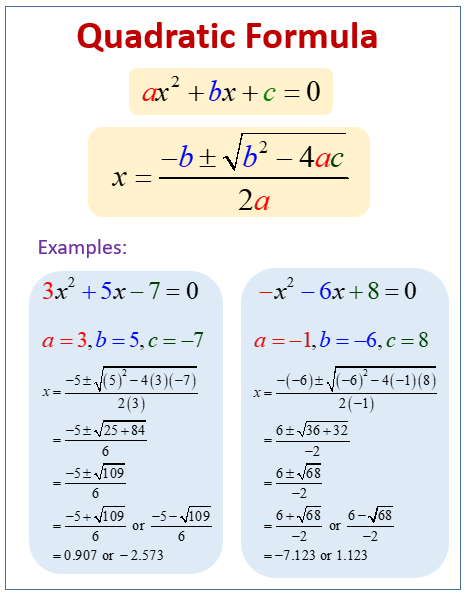
In this expression, the known values a = 3, b = 4 and c = 6 while x remains the unknown factor. The below chart show a few examples of a quadratic equation: Where x is a variable or an unknown factor, and a, b and c are known values. In complex numbers and quadratic equations, the standard form of a quadratic equation appears as: It is also known as ‘equation of a degree 2’ (because of x 2 ). It derives the name from the word ‘quad’ which implies square. Here, both a and b constitutes a complex number having a, as the real portion of the complex number and b acts as an imaginary one.Ī quadratic equation is a mathematical equation in algebra that comprises of squares of a variable. Real ones mostly comprise of 1, 1998, 12.38, whereas imaginary numbers generate a negative result when they get squared.įor instance, consider an equation in the form (a + ib). Complex numbers are nothing but a combination of two numbers (real, imaginary). Let us take a tour for a better understanding.Ī mathematical equation having a complex number comprises of the real and imaginary sections. If you get stuck with cumbersome mathematical problems, try seeking complex numbers and quadratic equations NCERT solutions. It comprises of linear and quadratic equations along with roots related to the complex number’s set (known as complex roots).Īlthough maths is a scoring subject, yet we find problems tricky because of insufficient knowledge of different topics. Complex numbers and quadratic equations is a segment of maths that deals with crucial theorems and concepts along with various formulae. Mathematics includes a lot of topics that give an edge to your problem-solving abilities and critical thinking. If students can remember some simple generalizations about roots, they can decide where to go next.A Guide to the Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Loh believes students can learn this method more intuitively, partly because there’s not a special, separate formula required. It’s quicker than the classic foiling method used in the quadratic formula-and there’s no guessing required. When solving for u, you’ll see that positive and negative 2 each work, and when you substitute those integers back into the equations 4–u and 4+u, you get two solutions, 2 and 6, which solve the original polynomial equation. When you multiply, the middle terms cancel out and you come up with the equation 16–u2 = 12. So the numbers can be represented as 4–u and 4+u. If the two numbers we’re looking for, added together, equal 8, then they must be equidistant from their average. Instead of starting by factoring the product, 12, Loh starts with the sum, 8. Those two numbers are the solution to the quadratic, but it takes students a lot of time to solve for them, as they’re often using a guess-and-check approach. “Normally, when we do a factoring problem, we are trying to find two numbers that multiply to 12 and add to 8,” Dr.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
